Below is an explanation of the various network types that are available and also the most common so that you immediately know which type you are working with.
What is a network:
A network is a system in which several computers are linked together. There are different types of networks, a company network often consists of a server and a number of computers (workstations). But there are also home networks, in which 2 or more computers are linked together.
There are also differences between connections, for example, there are mesh networks, star networks, bus networks,s and ring networks.
We will not go into this further as it is quite unnecessary information and often the star network is chosen.
LAN/WAN
Short-range networks are called local area networks (LAN, short for Local Area Networks). A LAN is located in a single room, building, or business area. Such a network is generally a connection of several PCs to a heavy computer system, which is called the server. Such a server contains one or more hard disks with a large storage capacity and fast accessibility time. These hard disks contain the application programs and the centrally stored data. However, networks can also extend over greater distances, for example, a city, a region, a country, or even worldwide. We then speak of a WAN, a Wide Area Network.
What can you do with a network:
- Many possibilities are possible with a network, including exchanging data over the network.
- Printers can be shared over the network and not every computer needs to have a cable connection to the printer.
What are the advantages of a network:
- Peripherals such as printers can be easily shared and save a lot of money on cables etc.
- The exchange of data is faster, you don’t have to put it on CD first, etc. You just copy it via the network. The size of these files does not matter, of course, there must be enough free space on the hard disk.
- Software only needs to be installed on 1 computer, it is possible to use the software via a network via 1 computer.
- The communication between the users over the network is better, it is possible to send messages and modify each other’s files.
What does a network look like:
A network can look very different, it also depends on the purpose for which it is used.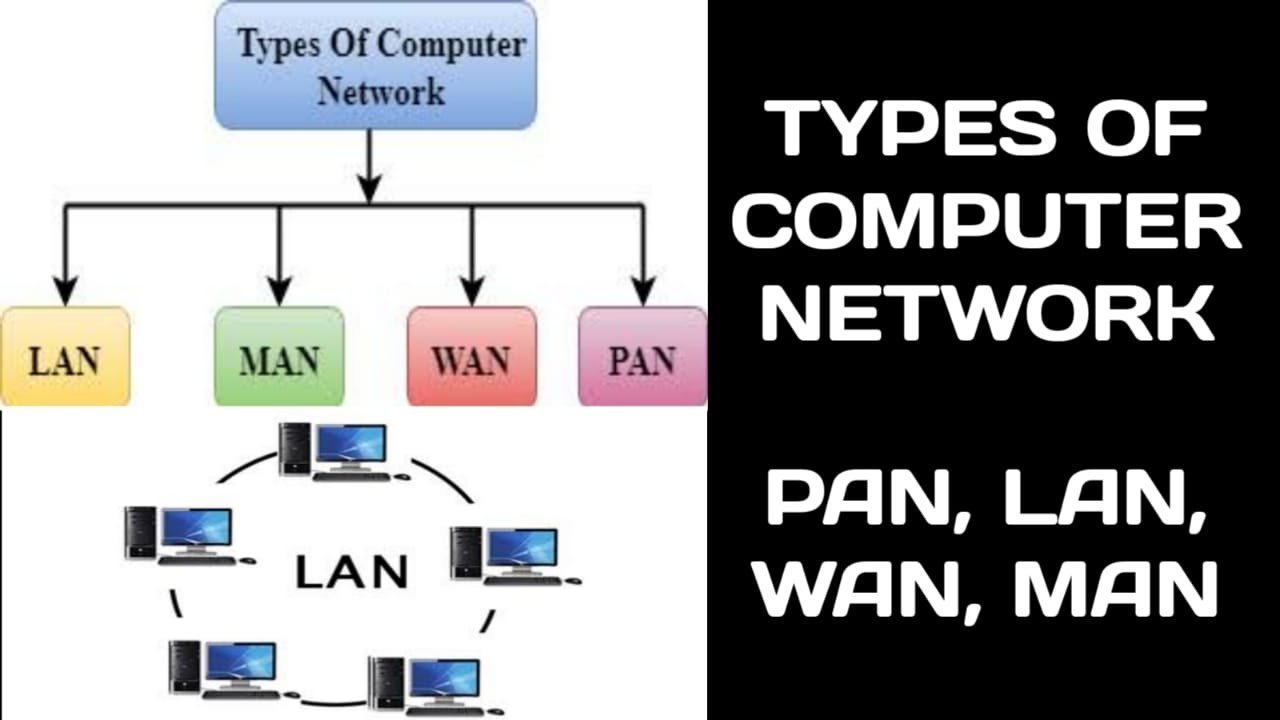
Cabling
The connection between the server and the workstations is formed by simple cables. In an office environment, the cables of a LAN are largely concealed. If the cable is interrupted anywhere, depending on the type of network, part of the LAN or the entire LAN can go down. In most cases, this means that business operations come to a standstill. In some situations, a wireless connection is used, but this requires a special network card in the PC.
Coaxial cable
A coaxial cable is very similar to the cable used for cable television at home. It consists of a copper or aluminum core surrounded by a second conductor, which is isolated from the core. Coaxial cables are suitable for transport speeds from 10 to 550mbps. Coaxial cables and their associated terminators and connectors are comparatively expensive. The connectors are called BNC connectors.
Reading Suggestions: The Best Mobile Wireless Chargers Of 2022
twisted pair
A twisted pair cable consists of twisted pairs of copper wires. A minimum of 2 pairs are used together to establish one connection. By twisting, the mutual influence of the veins is limited. The standard twisted-pair cable today consists of eight cores. We distinguish between UTP (Unshielded Twisted-Pair) and STP (Shielded Twisted-Pair), where UTP is further divided into seven categories. The throughput of the highest categories is about 2000mbps.
The advantages of STP, a shielded cable, are:
- Good shielding against radiation from outside
- Good shielding against radiation from itself
Optical fiber
Fiber optic cables are increasingly used as a means of transport for data. Glass fiber consists of a core of light-conducting material and a sheath of material with a different refractive index. The core is not made of glass, a synthetic fiber is used.
The advantages of fiber optic connections are:
- Very high throughput (minimum 200mbps)
- No problems with electromagnetic interference
- The fiber optic cable itself is cheap
However, the drawbacks are:
- Glass-copper connectors are expensive
- The installation of fiber optic cables is relatively expensive
- The cable must not lie in too sharp bends
- Repairing a fracture is only possible with special equipment
In practice, fiberglass is used in the following places:
- In companies where machines are used that cause a strong electromagnetic disturbance.
- In KPN’s network, all KPN exchanges are interconnected with fiber optic cables.
- When distances between 100 and 2000 meters have to be bridged.
We don’t find fiber optic cables much among the end user these days and given the high speeds that are currently possible via copper wire, the arrival of the fiberglass wall socket for the ordinary consumer will take a while. Perhaps that is no longer necessary: thanks to vastly improved compression techniques, it is now possible to send much more data within a certain time.
Wireless: no cabling
Sometimes it can be a problem to wire up a LAN in a particular office. A solution in such a case is the installation of a wireless LAN, in which case a LAN radio system is used to establish connections between various components. This may concern high-frequency and low-frequency radio signals. Other wireless LANs use infrared signals. In the case of a WAN, in addition to microwave systems that transmit radio signals, communication satellites can also be used. Satellites transmit microwave signals at a rate of several hundred million bits per second. Despite this, due to their distance from Earth, there is always a slight time delay.
Different types of connections:
Modem:
To establish a connection you need a device called a modem. Files can also be sent between 2 computers with this device. In data communication, digital signals are converted after analog signals. You also need the device for this. So the digital word is converted to analog, so it can be sent through a regular telephone line. This process is also known as modulation.
At the receiving computer, the analog signal is converted back to digital by the modem, then the computer can read the file. This process is also known as demodulation. A modem thus provides a connection between the telephone network and the PC. The speed at which a modem transmits data is called the transmission rate or transfer rate. Over the years, the speed has increased greatly by making the data messages more compact. Compared to modern cable, a telephone line is not really fast.
This is because the cable can transmit multiple bits synchronously. And sometimes it is also made more compact by an extraction program like Winzip. This reduces the size by 2/3 or ½. What is disadvantage is that if a malfunction occurs, everything has to be sent again. However, that is no longer the case because everything is quickly resolved or is automatically sent again. There are different types of connections, namely cable ISDN, ATM, and ADSL. Currently, especially the cable and ADSL and it is very popular with the consumer. We will come back to this later. Compared to modern cable, a telephone line is not really fast.
This is because the cable can transmit multiple bits synchronously. And sometimes it is also made more compact by an extraction program like Winzip. This reduces the size by 2/3 or ½. What is disadvantage is that if a malfunction occurs, everything has to be sent again. However, that is no longer the case because everything is quickly resolved or is automatically sent again. There are different types of connections, namely cable ISDN, ATM, and ADSL. Currently, especially the cable and ADSL and it is very popular with the consumer. We will come back to this later. Compared to modern cable, a telephone line is not really fast.
This is because the cable can transmit multiple bits synchronously. And sometimes it is also made more compact by an extraction program like Winzip. This reduces the size by 2/3 or ½. What is disadvantage is that if a malfunction occurs, everything has to be sent again. However, that is no longer the case because everything is quickly resolved or is automatically sent again. There are different types of connections, namely cable ISDN, ATM, and ADSL. Currently, especially the cable and ADSL and it is very popular with the consumer. We will come back to this later.
This reduces the size by 2/3 or ½. What is disadvantage is that if a malfunction occurs, everything has to be sent again. However, that is no longer the case because everything is quickly resolved or is automatically sent again. There are different types of connections, namely cable ISDN, ATM, and ADSL. Currently, especially the cable and ADSL and it is very popular with the consumer. We will come back to this later.
This reduces the size by 2/3 or ½. What is disadvantage is that if a malfunction occurs, everything has to be sent again. However, that is no longer the case because everything is quickly resolved or is automatically sent again. There are different types of connections, namely cable ISDN, ATM, and ADSL. Currently, especially the cable and ADSL and it is very popular with the consumer. We will come back to this later.
ISDN
Currently, ISDN is quite popular, people who cannot run cable often prefer ISDN. ISDN goes through a fully digital connection, so a modem is not necessary. Also, the files no longer need to be converted. Everything goes through the telephone line, there are 2 channels. The B and D channels, B channels are for telephony and data communication and the D channel is for signaling and control. The entire Dutch telephone network has now been digitized, and ISDN is possible almost everywhere.
ATM
ATM stands for Asynchronous Transfer Mode, the transfer capacities of existing networks have been increased via this connection. It doesn’t matter what kind of cable you have, fiber optic copper or coaxial cables. ATM increases speed and sends parcels in smarter ways.
Speed:
Whether it’s a network or the internet: all connections have their own speed. In this context, we do speak of the transmission speed. We express the speed in bps (bits per second), but you also come across the term Baud of the so-called Baud rate.
Using the Baud unit of measurement can be very confusing: it indicates how often the state (for example, the voltage) on a line can change. However, such a voltage state can also be intended for two bits (or more). Then 100 bits are transported, so the transmission rate is 100 bits per second.





























